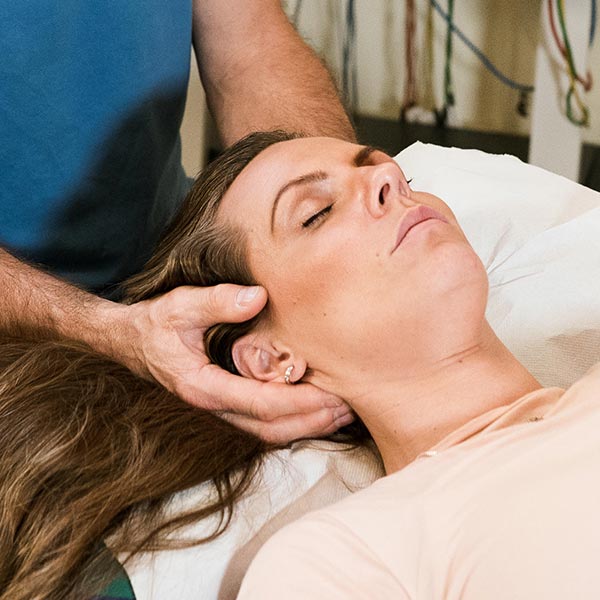
Osteopathy is a philosophyStill, Osteopathy carries some magic, which classic medicine sees critically. Over the last 20 years it has become a popular specialization. Essentially, Osteopathy is a precise manual interaction to create a reaction in the tissue. Amazingly, and in contradiction to the common thinking of therapists Osteopathy is a short intervention: "find it, fix it and leave it alone".
Osteopathy was first named 1874 by the medical doctor Andrew T. Still in Kirksville/US, while the country was suffering from an epidemic child disease. Through intensive study of the human body and influenced by Native American "bone-healers", he generated a new manual approach considering the whole body system, in particular the movement of fluids in tissues. He postulated health as a balanced equilibrium, which, in case of illness, can be restored by the hand of the practitioner and the response of the tissue. Andrew T. Still successfully healed meningitis in children (before antibiotics were developed). In practice, Osteopathy is a gentle anatomic touch with slight movement to release a healing reaction in the connective tissues, nerves and in the vascular system. This effect can help to restore structures and dysfunctions. The effects of age can be reduced and slowed down. Treatment should not be a long-term therapy, but rather be a precise intervention. Many years of training, good knowledge in anatomy, a sensitive touch and profound experience as a practitioner is the foundation for success. Any restriction in the body can lead to a pain syndrome or dysfunction. Dysfunction or reduced mobility in tissues can damage structures. "Function requires structure and structure requires function". The goal of the treatment is to regain a full mobility and to thus improve the body's self-healing reaction. ("Life in motion" by Rollin E. Becker) |
How does it works:
Osteopathy can be effective in:
www.osteopathie.de www.dgom.info |
|
Motion Praxis Sportorthopädie
Dr. med. Carsten Schlünsen D.O.M. Clayallee 161 14195 Berlin info@motion-praxis.de Tel +49 30 83206006 Mobil +49 178 2839650 |
|